The power system sector is undergoing an unprecedented transformation. Electricity distribution, a cornerstone of this industry, faces complex challenges such as the growing bidirectionality of power flows driven by renewable self-consumption, the need to maintain power quality, fraud prevention, and managing new grid connections. This dynamic landscape has ushered in a paradigm shift: the digitalization of distribution networks.
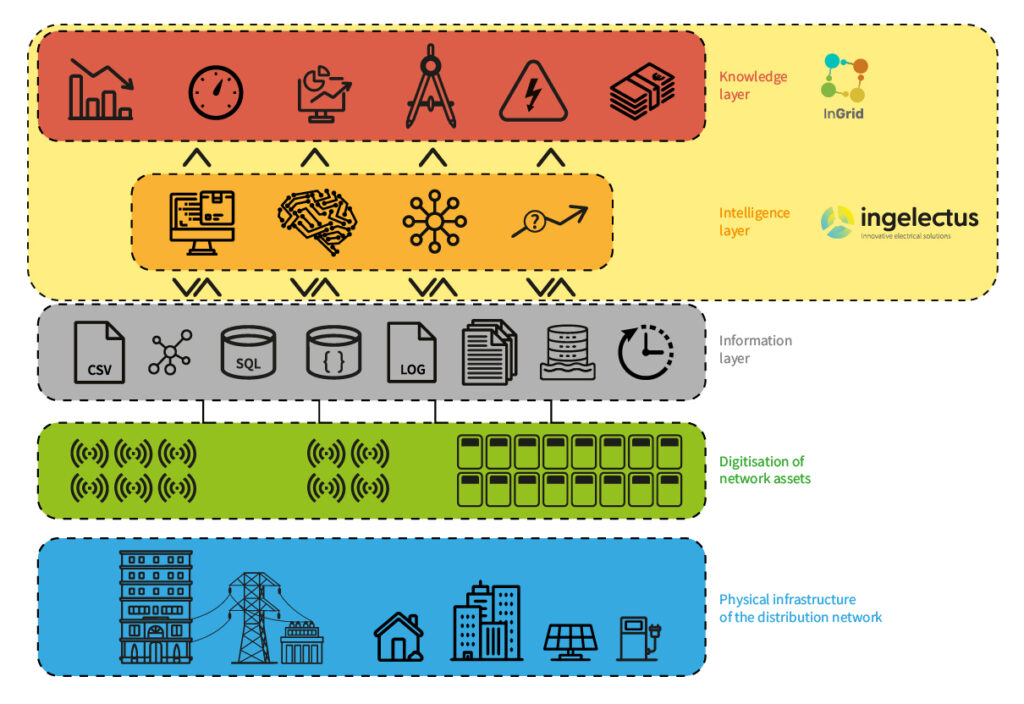
Digitalization is not merely about installing sensors or updating systems; it is a comprehensive process that reshapes how electric networks are operated and managed. It requires a mindset shift, advanced tools, and a strategic vision to create genuine Smart Grids. This transformative journey involves five fundamental stages:
The proliferation of renewable energy, ranging from residential solar panels to medium voltage generation plants, has disrupted traditional norms. Networks, originally designed for unidirectional power flows, must now handle bidirectional flows, congestion, and overvoltage challenges.
Digitalized networks offer the ideal solution. Technologies such as Advanced Distribution Management Systems (ADMS), intelligent sensors, and artificial intelligence enable:
Digitalization revolutionizes the operation and planning of electric distribution networks, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. These technologies enable real-time issue detection, minimize disruptions, optimize maintenance, prevent fraud, and improve capacity management. Additionally, they support sustainability by integrating renewable energy, reducing technical losses, and optimizing resource utilization.
Digitalization also facilitates regulatory compliance by ensuring transparency, resilience, and sustainability, meeting quality standards, minimizing losses, and reducing emissions. Furthermore, advanced tools support data-driven decision-making through data analysis and visualization of network behavior.
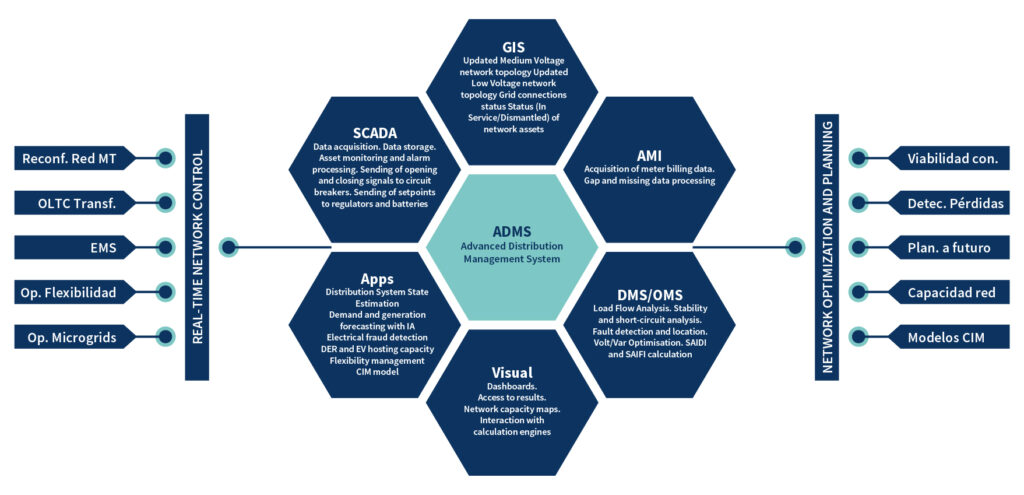
The future of electric distribution hinges on the ability to integrate renewable energy, electrify demand, and manage real-time data. Advanced Distribution Management Systems (ADMS), combined with AI and integrated platforms like GIS and SCADA, are emerging as the core of modern operations.
Digitalization is not just a technical requirement but also a strategic opportunity to lead the energy transition toward a more sustainable, efficient, and decentralized model. By adopting these tools and approaches, utilities can ensure more reliable power supply, meet regulatory requirements, and adapt to the demands of an increasingly electrified world.